
Actinolite, a mineral belonging to the amphibole group, has a rich geological history.
While valued for its aesthetic appeal, actinolite’s dark side involves its association with asbestos.
In this article, we delve into the origins, appearance, historical uses, and the darker implications associated with actinolite, aiming to unravel the complex nature of this mineral.
Table of Contents
What is Actinolite?
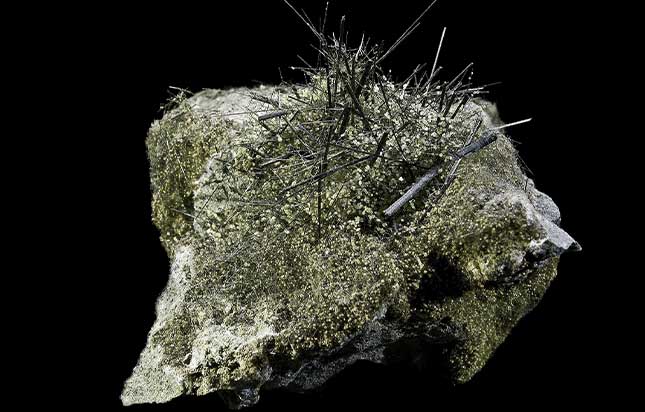

Actinolite, a member of the amphibole group of minerals, boasts a complex chemical composition.
It falls within the silicate mineral class, characterised by its structural arrangement of silicon and oxygen atoms.
The chemical formula for actinolite is:
(Ca2)(Mg,Fe)5Si8O22(OH)2
It is a combination of calcium, magnesium, iron, silicon, and oxygen elements.
This mineral’s distinctive crystal structure forms elongated prismatic crystals, contributing to its unique appearance.
However, actinolite has a darker side when it comes to asbestos.
Certain varieties of actinolite, when present as asbestos, pose serious health risks.
Asbestos-containing actinolite, if disturbed, releases microscopic fibres that can be inhaled, leading to asbestos-related diseases.
The duality of actinolite, admired for its aesthetic qualities and feared for its association with asbestos, underscores the importance of responsible handling and awareness.
What does Actinolite Look like?
Actinolite presents a distinctive appearance with a range of colours and a unique crystalline structure.
Typically in shades of green, or even black, this mineral’s visual allure is characterised by its fibrous or columnar texture.
Its crystal structure forms elongated prismatic crystals that often take the shape of needle-like fibres, giving actinolite a recognizable fibrous appearance.
In certain instances, it can occur in radiating clusters or granular masses.
While actinolite’s visual characteristics make it sought after for decorative purposes, it is crucial to ensure its safe handling.
Asbestos-related health risks are associated with certain forms of actinolite, emphasising the importance of accurate identification to ensure responsible handling and use in various applications.
What was Actinolite Used For?
Actinolite has somewhat of a dual history, depending on its uses:
Gemstone Properties of Actinolite
Actinolite, admired for its aesthetic appeal, has been historically utilised in ornamental arts and jewellery.
Its rich dark green to black colours make it an aesthetic gemstone choice for decorative items.
Actinolite’s unique crystal structure allows for detailed craftsmanship, contributing to its popularity in the creation of cultural artefacts and jewellery pieces.
Asbestos Uses
Certain varieties of actinolite have been exploited for their unique properties in various industries.
Actinolite asbestos, with its heat-resistant and durable characteristics, found applications in construction materials like insulation, cement, and fireproofing.
The fibrous nature of asbestos actinolite made it a valuable component in textiles and friction materials, enhancing their strength and resistance to heat.
However, the use of asbestos has significantly diminished due to its established health hazards.
Inhalation of asbestos fibres, including those from actinolite, poses severe risks, leading to respiratory diseases and cancers.
The detrimental health effects have prompted a shift away from the use of asbestos-containing actinolite in favour of safer alternatives, emphasising the importance of responsible handling and awareness in industries historically associated with asbestos use.
Where is Actinolite Found?

Actinolite is found in various geological settings worldwide, contributing to its global presence.
In Austria, actinolite deposits are notably situated in the Eastern Alps, showcasing the mineral’s affinity for mountainous regions.
Russia, particularly in the Ural Mountains, hosts significant occurrences of actinolite, adding to the mineral diversity in this vast country.
Norway is another location where actinolite can be encountered, with geological formations providing suitable conditions for its formation.
The United States, particularly in states like Vermont and North Carolina, contains actinolite deposits, contributing to the country’s mineralogical diversity.
In Canada, actinolite occurrences are documented, aligning with the country’s rich geological landscape.
Lastly, China stands out as a notable location for actinolite, emphasising its prevalence in diverse geological settings globally.
These worldwide occurrences underscore the mineral’s adaptability to different geological conditions, making it a fascinating subject for geological exploration and appreciation.
How to Identify Actinolite Asbestos
While actinolite in its pure form is a harmless mineral, certain varieties are associated with asbestos.
Identifying actinolite asbestos can be done with several methods:
Microscopic Analysis
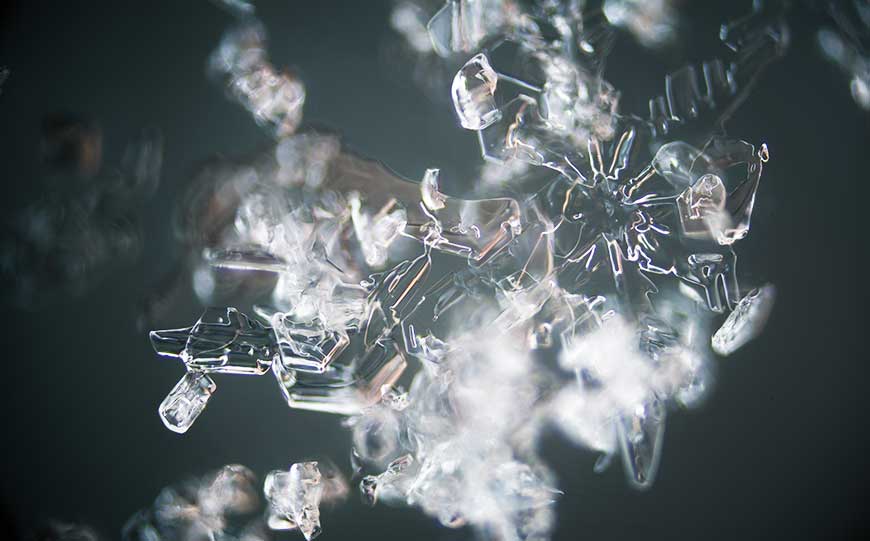

To accurately identify actinolite asbestos, microscopic analysis is essential.
Asbestos fibres are too small to be visible with the naked eye, necessitating advanced techniques for examination.
Fibrous Structure
Asbestos actinolite retains the fibrous structure common to actinolite but with potentially hazardous implications.
The fibres can be elongated and needle-like.
Colour Variation
While actinolite asbestos shares the dark green to black colour range with pure actinolite, variations in colour intensity or the presence of impurities may be indicative of asbestos content.
Asbestos Testing Kits
For individuals concerned about potential asbestos presence, asbestos testing kits are available.
These kits typically involve collecting samples and sending them to a certified laboratory for analysis.
Professional Inspection
Engaging the services of professionals, such as an asbestos surveyor, for a thorough inspection is usually necessary.
Trained experts can conduct comprehensive analyses, ensuring accurate identification and addressing potential risks associated with actinolite asbestos.
For more information about professional asbestos identification, get in touch with us here at KD Asbestos.
Awareness of Geological Context
Understanding the geological context is crucial.
Asbestos-containing actinolite is more likely to be found in specific geological formations, aiding in targeted identification efforts.
What are the Dangers of Actinolite?
Actinolite asbestos poses serious health risks when its fibres become airborne.
Inhalation of these microscopic fibres can lead to several health issues.
Respiratory Health Risks
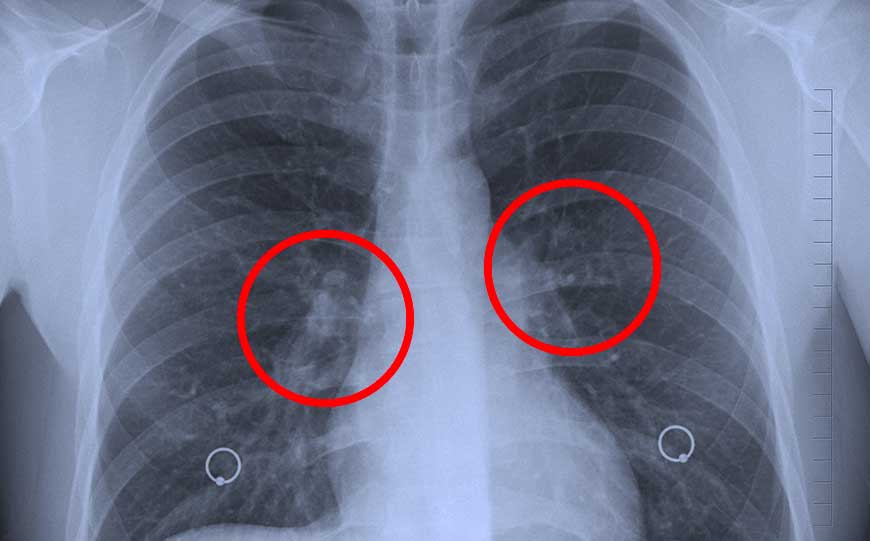
Actinolite, specifically in its asbestos form, poses severe respiratory health risks.
Asbestos exposure and the inhalation of asbestos fibres can lead to various respiratory diseases, including lung cancer, and mesothelioma.
Carcinogenic Potential
Actinolite asbestos has been identified as a carcinogen, particularly linked to lung cancer.
Prolonged exposure to airborne asbestos fibres increases the risk of developing these life-threatening conditions.
Asbestosis
Inhalation of actinolite asbestos fibres can cause asbestosis, a chronic and progressive fibrotic lung disease.
This condition results from the body’s inability to break down or remove the inhaled asbestos fibres.
Long Latency Period
One of the insidious aspects of actinolite asbestos exposure is the long latency period between initial contact and the manifestation of diseases.
Diseases may take decades to surface, making early detection and prevention challenging.
Occupational Hazards
Occupations associated with industries that historically used asbestos, such as construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing, pose a higher risk of exposure to actinolite asbestos.
Workers in these industries need to adhere to strict safety protocols.
Environmental Exposure
Individuals residing near natural actinolite deposits may face environmental exposure.
While the asbestos content in natural deposits is typically lower than in industrial applications, precautions should still be taken.
Secondary Exposure Risks
Workers exposed to actinolite asbestos can unknowingly bring home asbestos fibres on their clothing, leading to secondary exposure risks for family members and communities.
Regulatory Measures
Recognising the dangers of actinolite asbestos, regulatory measures have been implemented to restrict its use.
Compliance with safety standards, asbestos removal protocols, and occupational guidelines is essential in mitigating risks.
Educational Awareness
Raising awareness about the dangers of actinolite asbestos is crucial.
Educating the public, especially those in high-risk occupations, about proper safety measures and the potential health consequences is key to preventing exposure and minimising associated risks.
Conclusion
Actinolite is a mineral of dual nature — admired for its beauty in its natural form and dreaded for its association with asbestos.
While its contribution to ornamental arts and cultural artefacts is noteworthy, the potential health hazards linked to actinolite asbestos underscore the importance of informed handling and awareness.
As we appreciate the geological wonders of actinolite, it is crucial to navigate its complexities responsibly, ensuring the safety of both its admirers and those who encounter it in various contexts.